- Arizona
- Florida
- Texas
- Prenatal cannabis use disorder and infant hospitalization and death in the first year of life, 2023, January 1
Arizona
Arizona child Fatality Review Team
Twenty-Seventh Annual Report
November 15, 2020
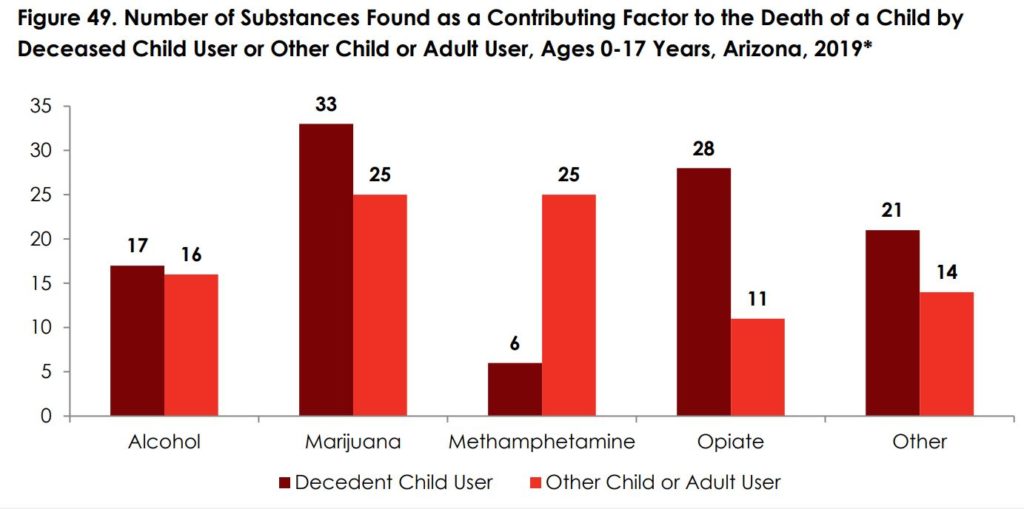
In 88% of the 119 substance use related deaths (n=105), the decedent child was using or abusing alcohol or drugs which caused or contributed to their death (Figure 49). Marijuana and opiates were the most common substances which caused or contributed to the death of the child were the child was the user. In 76% of the 119 substance use related deaths (n=91), another individual (child or adult) was using or abusing alcohol or drugs which caused or contributed to the death of the child.
Florida
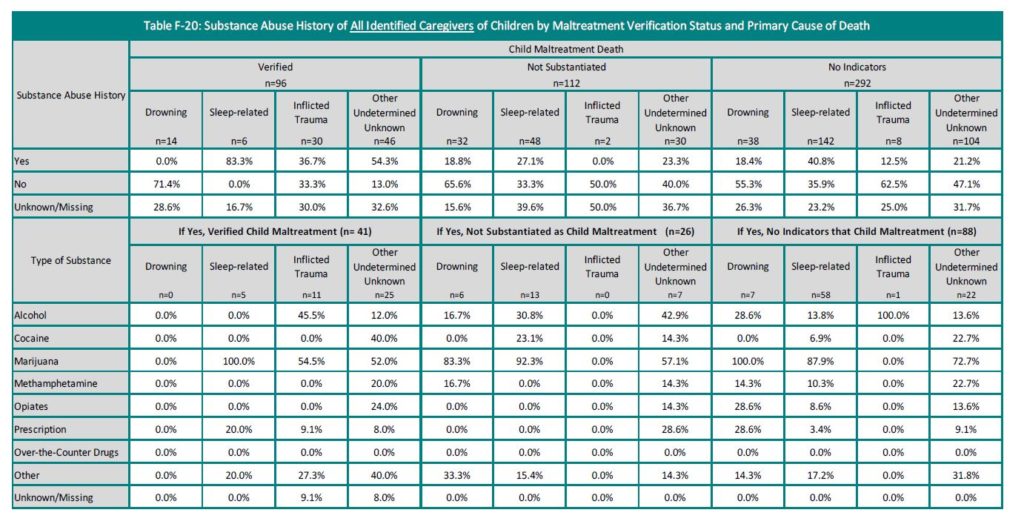
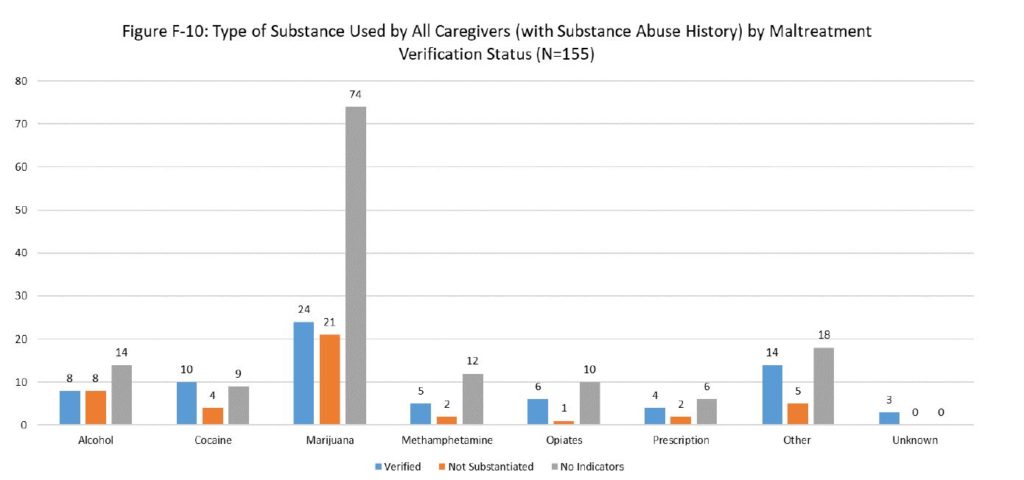
Substance Abuse History of Caregivers and Supervisors
For those with a substance abuse history, most of all caregivers of children whose deaths were verified as maltreatment has a history of marijuana use (form a low of 52% for other causes to high of 100% for sleep-related deaths.) Similarly, high percentages of caregivers use of marijuana are observed for all primary causes of death for not substantiated and no indicators of maltreatment deaths; from a low of 0.0% for not substantiated inflicted trauma deaths to a high of 83.3% for not substantiated drowning deaths.
Page 148 http://www.flcadr.com/documents/CADR2020AnnualReportFINAL.pdf
Texas
Department of Family and Protective Services
Fiscal Year 2023, Child Maltreatment Fatalities and Near Fatalities Annual Report
March 2024
Substance Abuse by Caregiver as Risk Factor
Substance Use and Substance Abuse Disorder by Caregiver as Risk Factor
During the review of confirmed child fatalities due to abuse and neglect, cases were reviewed
for a documented history of substance use (including inappropriate use of prescribed
medications) and for active concerns for substance use at the time of the child fatality.
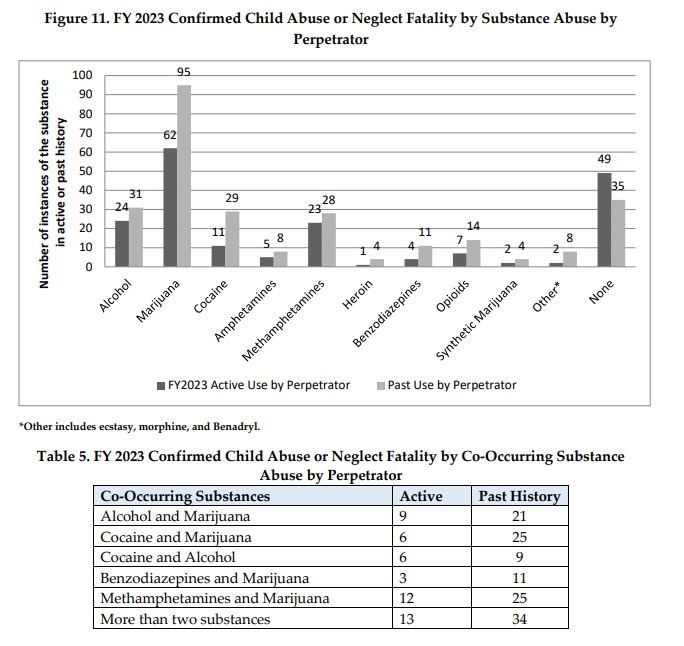
For FY 2023, 114 of the 164 child fatalities caused by abuse or neglect involved a parent or
caregiver actively using a substance and/or under the influence of at least one substance that
affected the ability to care for the child. In the tables and chart below, the substance abuse is
described by type and if it was reported. While methamphetamine use and alcohol use was
identified in 24 child fatalities, marijuana was the substance most identified as an active
substance in child abuse and neglect-related fatalities and was identified as prior use in 95 of
the cases.